Abstract
Speech-driven 3D facial animation synthesis has been a challenging task both in industry and research. Recent methods mostly focus on deterministic deep learning methods meaning that given a speech input, the output is always the same. However, in reality, the non-verbal facial cues that reside throughout the face are non-deterministic in nature. In addition, majority of the approaches focus on 3D vertex based datasets and methods that are compatible with existing facial animation pipelines with rigged characters is scarce. To eliminate these issues, we present FaceDiffuser, a non-deterministic deep learning model to generate speech-driven facial animations that is trained with both 3D vertex and blendshape based datasets. Our method is based on the diffusion technique and uses the pre-trained large speech representation model HuBERT to encode the audio input. To the best of our knowledge, we are the first to employ the diffusion method for the task of speech-driven 3D facial animation synthesis. We have run extensive objective and subjective analyses and show that our approach achieves better or comparable results in comparison to the state-of-the-art methods. We also introduce a new in-house dataset that is based on a blendshape based rigged character.
Video
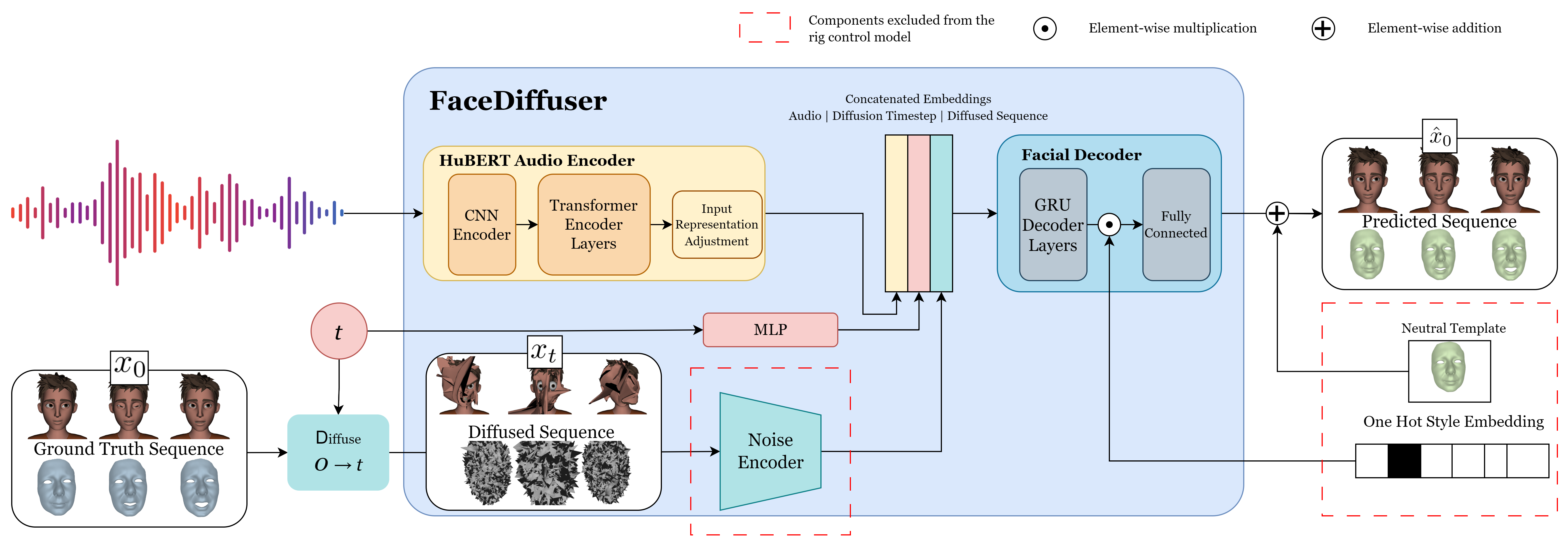
Methodology - Training
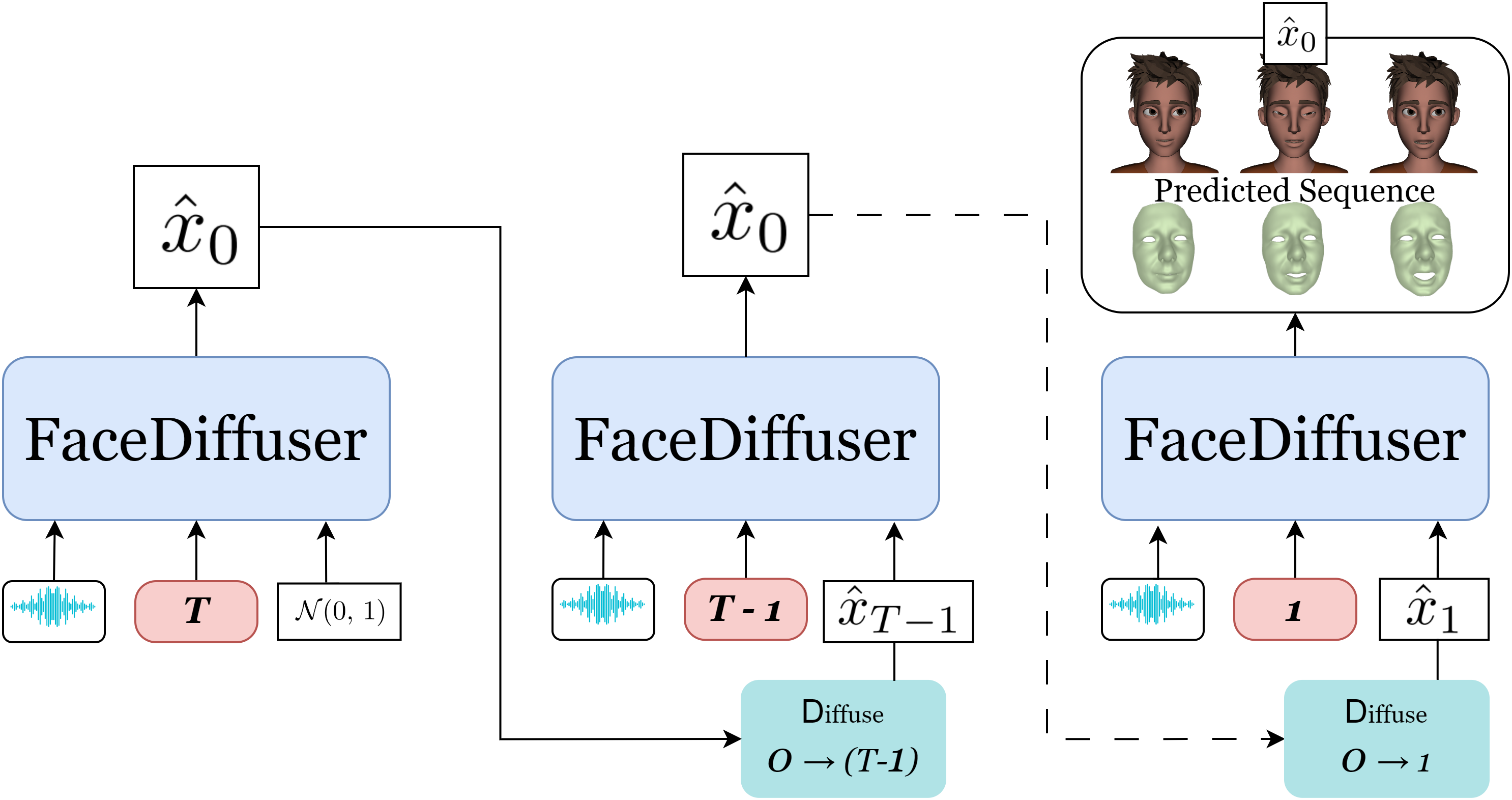
Methodology - Inference
BibTeX
@inproceedings{FaceDiffuser_Stan_MIG2023,
author = {Stan, Stefan and Haque, Kazi Injamamul and Yumak, Zerrin},
title = {FaceDiffuser: Speech-Driven 3D Facial Animation Synthesis Using Diffusion},
booktitle = {ACM SIGGRAPH Conference on Motion, Interaction and Games (MIG '23), November 15--17, 2023, Rennes, France},
year = {2023},
location = {Rennes, France},
numpages = {11},
url = {https://doi.org/10.1145/3623264.3624447},
doi = {10.1145/3623264.3624447},
publisher = {ACM},
address = {New York, NY, USA},
}